Florida Strain Library
About the Different Marijuana Strains in Florida
Discover the array of marijuana strains available in Florida through the state’s cannabis dispensary brands. By clicking on each strain, you can explore the list of products specific to that strain and search by brand, product type, and strain type.
Florida cannabis dispensaries offer a diverse selection of marijuana strain types, including Sativa, Indica, and Hybrid strains. The Hybrid strains can range from Sativa-dominant to balanced to Indica-dominant. Additionally, Florida strains also feature High-CBD strains and CBD-only strains.
The Florida Strain Library is a new initiative. If you’ve tried any of the products, take a moment to rate and review the Florida strain products. Your feedback is highly appreciated. Thank you.

Florida Indica Strains

Indica Dominant Strains
Florida Sativa Strains

Sativa Dominant Strains
Cannabis Strain Types Explained
What Are The Differences In Strain Types?
Cannabis is a truly fascinating plant. Its resinous, aromatic female flower clusters produce scores of active compounds that can instantly change one’s state of mind and regulate an extensive variety of systems in the human body, especially the human brain. Furthermore, the balance of these compounds can be tweaked to accentuate or dampen these effects through selective breeding. These various breeds of cannabis are often referred to as strains.
In this post, we’ll look at what gives particular strains their superpowers and hopefully help our readers decide which strain will best serve particular medicinal needs or fit your recreational wish list.
Let’s begin by examining what it is about weed that makes it so effective at treating particular medical issues and at altering states of consciousness. Following that, we’ll be able to better appreciate why each individual strain packs its particular punch.
What’s in your weed?
So, what is it about cannabis that makes it so versatile a drug?
At least two types of compounds found in cannabis have medicinal benefits.
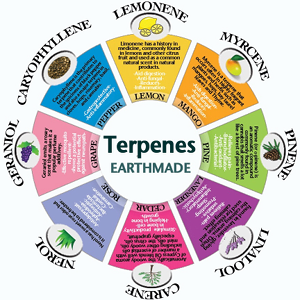
2 Types of Beneficial Compounds In Cannabis
- Cannabinoids
- Terpenes
The balance of these two classes of ingredients determines the particular set of effects of a strain. These categories of strains can be broken down into the following categories:
Categories of Cannabis Strains
- Sativa
- Indica
- Hybrid
- Hemp
First, let’s go over the two categories of medicinally beneficial compounds produced in cannabis. We’ll start with cannabinoids first and then discuss terpenes.
What are cannabinoids?
Back in the late 60’s when the popularity of marijuana started to ramp up due to the hippie movement, researchers began looking into what it is about marijuana, exactly, that gives it its euphoria-inducing qualities. What they discovered literally shocked the medical marijuana community.
It was a research team in Israel that discovered that compounds in cannabis interact with receptors on the surface of cells in all the major organs of the human body, especially the brain. They dubbed these compounds cannabinoids. And they labeled the overall system the human endocannabinoid system, or ECS, for short.
So what’s so shocking about that, you ask? The shocking part is that they discovered that the human body naturally produces its own cannabinoids. These were dubbed endocannabinoids, while those produced in cannabis are known as phytocannabinoids. What’s so amazing about this is that it stands to reason that the human body has co-evolved with cannabis, and that, quite likely, both types of cannabinoids are required to maintain balanced health. In other words, it’s no coincidence cannabinoids have such powerful effects on our minds and bodies.
Furthermore, this implies that depriving the human body of cannabinoids might be the cause of the drastic increase in some or even many of the variety of illnesses which are on the rise today. Researchers refer to this condition as endocannabinoid deficiency, however, it may also apply to a lack of phytocannabinoids in the diet.
Real quick history lesson for you here.
The fact of the matter is that humans have been utilizing cannabis for food since long before humans were even invented. A wide variety of animals feed on cannabis seeds and greens and have done so for eons. We’re talking hundreds of millions of years over which mammals evolved to take advantage of the power of cannabis. Furthermore, humans have been cultivating cannabis for use in food and medicine since the dawn of civilization thousands of years ago.
But that all changed for the human race when a handful of powerful politicians and businessmen decided to outlaw the plant staring back in the 1930s. But that’s another story altogether.
So that’s the quick history lesson. The point of the lesson is to illustrate the human race has gone without cannabis in their diets for only the past eight decades or so. And depriving ourselves of phytocannabinoids might be the cause of the rise in the incidence of many modern ailments.
Now back to cannabinoids and their medicinal properties.
Earlier we mentioned the human endocannabinoid system. The ECS consists of two parts — endocannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors on the surface of cells which interact with cannabinoids. Endocannabinoids are produced at nerve synapses in the brain. And cannabinoid receptors are found in abundance in the brain and other major organs.
There are two types of receptors — CB1 receptors which are mostly found in the brain, and CB2 receptors which are found throughout the body. Hold onto that information for a moment.
Scores of different cannabinoids are produced by cannabis. The most abundant cannabinoid found in marijuana is known as delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC. This is the compound that causes people to feel euphoric. THC molecules have the exact structure required for them to bind with the CB1 receptors in the brain resulting in altered states of consciousness. (We’re not going to get into the details of how that works here.)
The second most abundant cannabinoid in marijuana is known as cannabidiol, or CBD. Although CBD does not bind with cannabinoid receptors, it does interact with them and effects both how the brain produces endocannabinoids and other neurotransmitters and how receptors react to them.
In recent years it has been discovered that CBD has the ability to modulate how CB1 receptors respond to THC. It also has the ability to mimic one of our own naturally produced endocannabinoids known as anandamide. Anandamide is responsible for modulating the production and uptake of another compound known as serotonin. Serotonin is, in turn, responsible for regulating brain activities such as stress response and moods. CBD also effects systems such as sleep cycles, immune response, pain response, and so on.
There are also scores of other lesser cannabinoids produced in cannabis which each has its own slightly different chemical structure and its own set of effects on the human brain and body.
In addition to having effects on the brain and central nervous system, cannabinoids are also closely involved in regulating the immune system and have been proven to impart powerful anti-inflammatory effects. Inflammation is the major cause of pain. Reduce inflammation and you reduce pain. Inflammation is also indicated in cardiovascular conditions such as heart disease and arteriosclerosis, or narrowing of the arteries.
Cannabinoids are also known to have antioxidant, antibiotic, antiviral, antifungal properties. Essentially the biochemical structure of cannabinoids allows it to latch onto molecules in germs thereby rendering them harmless.
So, let is suffice to say that the balance of cannabinoids produced in each particular strain of cannabis determines how CB1 receptors in the brain and CB2 receptors in the body respond. Some strains are very high in THC and very low in CBD. These strains affect the mind more than the body. And some strains are higher in CBD and lower in THC and affect the body more than the mind.
Just a side note: THC is considered to be a psychotropic compound. It actually changes perception of reality. CBD is often mistakenly labeled as a non-psychoactive compound, but it does affect moods and is therefore technically psychoactive.
So that’s the weird world of cannabinoids in a nutshell. Now, let’s take a look a second family of compounds produced in cannabis which are collectively known as terpenes.
What are terpenes?
While cannabinoids are observed in relatively high concentrations in cannabis flowers, in some cases approaching as high as 25% or more of a bud’s weight, terpenes, on the other hand, are measured in parts per million. But microscopic quantities of terpenes can produce significant effects on the human body.
And while cannabinoids are essentially odorless, terpenes are highly volatile and are responsible for the distinctive scents and flavors of each strain of cannabis. The term volatile simply means that they evaporate easily and therefore quickly find their way to your nose. If you’re ever in a room where someone opens a container of extremely strong-smelling weed, the moment the scent arrives, your mood begins to change. It happens almost instantly.
Terpenes evolved in plants for a number of purposes, the most important of which is to attract pollinators such as bees and butterflies and to repel pests such as plant-eating insects. In order to achieve these goals, terpenes must have the power to affect the physiology of insects and other animals, including mammals.
Just as with cannabinoids, cannabis is capable of producing scores of various terpenes. Each of them has its own fragrance and its own set of effects on the human body. Some terpenes make us feel more awake and focused, others make us feel more relaxed, some have anti-inflammatory properties and some have antibiotic properties, and so on.
We’re not going to get into the variety of terpenes found in cannabis here since we’re here to talk about strains and their effects, but you can learn more about terpenes here.
As with cannabinoids, the balance of terpenes in a particular strain plays a large role in the overall effects of a strain. In fact, certain terpenes affect how cannabinoids interact with cannabinoid receptors. This combined effect of the variety of cannabinoids and terpenes found in cannabis is often referred to as the entourage effect. An entourage is a organization of people that travel and work together to achieve their purpose. And so it is with cannabis.
The point to take away here is that the balance of cannabinoids and terpenes can be adjusted through breeding to achieve particular overall effects.
Now that we know what gives various strains their individualized properties, let’s look at some categories of strains and get into their common medicinal uses.
Indica vs. Sativa Strains
So what plant is being bred to create the diverse strains of marijuana?
Technically, all cannabis that is cultivated today for medicinal and recreational use is the same species: Cannabis sativa L. However, over the eons, this species has evolved differently in different parts of the world with diverse geographies and climates. The strains that evolved in Asia and Africa are commonly referred to as indica strains, while those that evolved in the Americas are known as sativa strains.
Physically speaking, indica plants are bushier with wider leaves and larger buds while sativas are slimmer with skinnier leaves and thinner buds.
Chemically, the main difference between sativas and indicas is the balance of cannabinoids and terpenes.
Pure indica strains can be bred to increase or decrease particular active compounds, as can pure sativa strains. Because of this pure strains are not all alike. Furthermore, these two divisions of strains, because they are technically the same species, can also be interbred to produce hybrids of the two which can drastically alter the balance of these compounds creating distinctly unique strains.
That’s probably enough science for one article. Let’s go ahead and talk about the various strains of cannabis and why you might choose one over another.
Sativa: The Head High
Pure sativa strains tend to have a sweet and spicy scent and are known for their “buzz” effect. Sativas are generally better for daytime use than indicas as the effects tend to be more invigorating, uplifting, and creative.
In terms of effects, sativas are known to be more energizing and produce more of a head high. By that, we mean that sativas are more likely to alter conscious perception than indicas. At the same time, because they are lower in CBD and certain terpenes, they are less likely to produce effects such as sleepiness.
Sativas are generally high in a terpene known as limonene, which can have anti-depressant effects, and pinene, which is known to have anti-inflammatory properties.
For the reasons mentioned above, sativa strains are preferred when engaging in physical activities as well as creative pursuits. Some of the activities which lend themselves more to sativas include:
- Outdoor activities such as hiking
- Creative activities such as music and art
- Social activities
- Concerts, comedy shows, etc.
- Sports events
- Arts festivals
Medicinally speaking, sativas are used to treat conditions such as:
Potential unwanted side effects include:
- Anxiety and paranoia
- Mind racing
- Over-analyzing
- Hysteria (laughing or crying)
Pure sativa strains include:
One word of warning on sativas that’s worth repeating. They can have powerful effects on consciousness. Taken in high doses sativas can produce unwanted side effects such as nervousness, paranoia, anxiety, and hysteria.
Indica: The “Chillaxing” High
Pure indica strains tend to have what’s commonly described as a skunky or diesel-like odor and are known for their relaxing and mood-altering effects. Because these strains are higher in CBD they tend to mitigate the brain buzz somewhat and bring about more of a “stoned” feeling and deep relaxation. Indicas tend to have a sedative effect and are generally preferred for night-time use.
A common terpene found in indicas known as myrcene has an earthy aroma and is thought to amplify the sedating effects of indicas. Another is linalool, which is believed to help relieve anxiety.
In terms of recreational use, indicas are less desirable for those with active lifestyles. However, they are more desirable for times when you just want to eat pizza and watch Netflix.
Some of the activities that might benefit from an indica strain are:
- Relaxing at home
- Watching TV and streaming movies
- Listening to music
- Relaxing outdoors
Medicinally speaking, indicas are known for their stress-busting properties. Indicas are often used to help reduce anxiety and hyperactivity and are also used to treat conditions such as:
- PTSD
- Stress
- Sleep disorders
- Muscle tension
- Nausea
- Acute pain
- Depression
Potential unwanted side effects of indicas include:
- Lethargy, laziness
- Tiredness, sleepiness
- Mind-numbing
- Overeating and lack of exercise
Popular pure indica strains include:
Hybrid Strains: The Middle Grounds
To produce a hybrid strain, a pure sativa is interbred with an indica strain. Hybrids can also be interbred with each other. Hybrids often take on some of the properties of both indica and sativa. Sativa dominant hybrids tend to be higher in terpenes that induce wakefulness and increase focus. Indica dominant hybrid strains tend to be higher in terpenes known to induce relaxation.
Some of the more well-known hybrid strains include:
Low-THC Strains
Certain strains of marijuana have been bred specifically to be low in THC and high in CBD. Some of these strains offer as much as 25 parts to 1 CBD to THC. Low-THC, high-CBD cannabis strains are becoming more and more popular and are great for people who don’t want the buzz that comes with most strains of marijuana.
Though they are generally not used for recreational purposes, Low-THC strains are great for relieving stress and tension. Furthermore, the fact that these strains still have some THC in them makes them more beneficial than THC-free strains for a number of therapeutic uses, especially neurological disorders.
Low-THC strains are often used to improve mood and help with relaxation.
Medicinal uses of low-THC strains:
- Neurological disorders
- Fatigue
- Fibromyalgia
- Muscle Spasms
- Arthritis
- Stress
- Depression
- Anxiety
- PTSD
- Insomnia
- Digestive issues
- Nausea
- Pain
Low-THC, high-CBD strains include:
- Charlotte’s Web (20% CBD, <1% THC)
- Harle-Tsu (22% CBD, <1% THC)
- Ringo’s Gift (20% CBD, <1% THC)
- ACDC (19% CBD, <2% THC)
- Harlequin (15% CBD, 6% THC)
Note: The percentages listed above can vary substantially.
Balanced 1:1 THC:CBD Strains
There are a number of strains available today that tend to have equal or close to equal levels of CBD and THC referred to as Balanced Hybrid Strains. These strain provide the best of both worlds, so to speak.
- Sour Tsunami (11% CBD)
- Stephen Hawking Kush (22% CBD)
- Warlock (13% CBD)
THC-Free Hemp Strains
Any strain of cannabis which produces less than 0.3% THC falls out of the category of marijuana and into the category of hemp. Because hemp is non-intoxicating, marijuana and hemp are governed by two different sets of federal laws and agencies, as is the case in most states. While marijuana is generally regulated like a controlled substance, hemp is now regulated by state and federal agricultural agencies.
To clarify further, there are two types of hemp. First, there’s the kind used to produce fibers and seeds which is often referred to as industrial hemp. Industrial hemp produces very low levels of cannabinoids and is not extremely useful as a drug.
Strains of hemp used to produce CBD are commonly referred to as phytocannabinoid-rich hemp, or PCR hemp. Although these strains are non-psychotropic and not very useful for recreational purposes they are extremely useful in medicine.
PCR hemp strains include:
- Charlotte’s Cherries
- Berry Blossom
- Cobbler
- Trophy Wife
- Chardonnay
Note: These strains are often used to produce CBD oil.
Choosing a Strain
We’ll cap this feature off with some advice for how to choose the ideal strains for your medical conditions and lifestyle.
If you’re choosing between a pure indica and a pure sativa, the choice is clear:
- Indicas can be extremely relaxing and are best for nighttime use.
- Sativas can be uplifting and invigorating and are best for daytime use.
If you’re thinking of going with a hybrid the only advice we can give you here is to do your homework and learn about the various effects of each hybrid strain available to you, and also make sure you talk to a knowledgeable budtender who is intimately familiar with the strains they are selling.
If you’re concerned about failing a drug test, or roadside sobriety test, or you just don’t want the buzz that comes with THC, then you should stick to high-CBD, THC-free PCR hemp strains. Smokable THC-free buds are not common. Most patients simply use CBD tinctures, capsules, and vape oils, or CBD-infused edibles, but pure CBD dabs are also available. Keep in mind that these products don’t always contain additional cannabinoids and terpenes. Some are made with purified CBD and will lack many of the benefits provided by terpenes. On the other hand, you may not want terpenes. (Some people are actually allergic to certain terpenes.) So, once again, you have to do your homework.
And, a final word of warning: If you’re using cannabis for medicinal purposes, it’s not wise to buy marijuana off the street. Unless you’re experienced enough to identify a strain and its probable effects by its look and smell, you won’t know what strain your getting. And oftentimes pot dealers either don’t know what strain they are carrying, or they have it wrong. If you have no other choice but to buy on the street, then you’ll just have to experiment with what you have. If it makes you sleepy, use it sparingly before going to work or school or before sports or social activities. If it keeps you awake and gets your mind racing, use it sparingly at night.
Finally, cannabinoids and terpenes are both involved in highly complex physiological systems and will have different effects on different individuals. So if a friend says a strain helps them sleep, it might not help you sleep. Of if it relieves their pain, it might not relieve your pain. The opposite is also true. Just because someone says a particular strain didn’t help them with a condition from which you are also suffering, that doesn’t mean it won’t help you.
The secret to success with cannabis is doing some experimentation, listening to your body, noting the effects, and adjusting accordingly. As they say, practice makes perfect!